Metabolism-Definition, Types, Examples, etc
Introduction
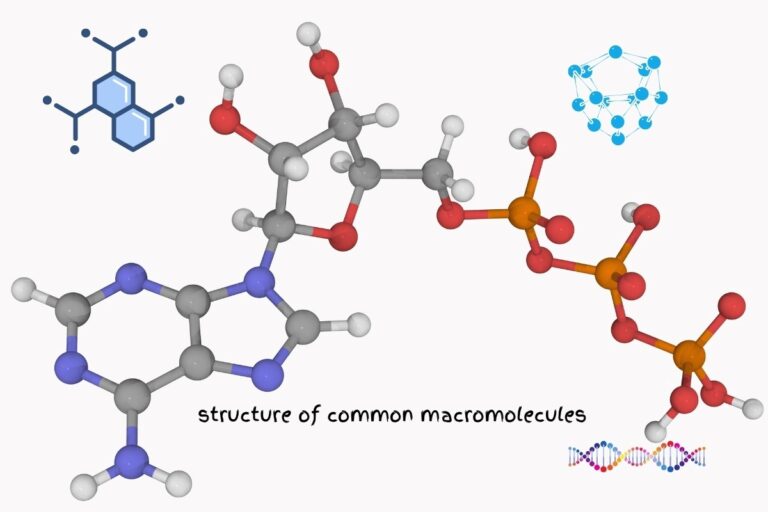
Metabolism is how cells can synthesize vitamins, hormones, and other substances from the nutrients they receive from digested food. The basic elements of metabolism include organic molecules (the products of living organisms), inorganic molecules (compounds like water or minerals), macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids, and energy.
This article will define metabolism, explore two types of it – catabolic and anabolic – give examples for each type, explain what organic compounds are used in your body’s metabolic processes, what inorganic compounds are used in your body’s metabolic processes. We’ll finish with how all these components work together to make up a healthy life!
Types of Metabolism
There are two types of metabolism: Catabolic and Anabolism.
Catabolic Metabolism


Catabolic metabolism breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones to be used as an energy source or to create other biological molecules. These molecules can be either organic or inorganic compounds. They include proteins, lipids (fats), carbohydrates (sugars), vitamins, minerals, and hormones.
Proteins are broken down into amino acids to create new proteins or break them down for energy purposes. Fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol to create energy or break them down for cellular purposes.
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose to create energy or break them down for cellular purposes. Vitamins and minerals are broken down into simpler compounds to be used by the body or broken down for energy purposes.
Hormones are broken down into simpler compounds to be used by the body, so these compounds are not included in the list of catabolic molecules.
The end products of the catabolic process can be either organic or inorganic molecules. They are used for energy, as precursors to synthesize other biological molecules, or for cellular purposes.
Anabolic Metabolism


Anabolic metabolism is the process of building complex molecules from simpler ones. In contrast to catabolic, anabolism requires energy and doesn’t break down molecules.
Anabolism is mostly the synthesis of complex lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These complex molecules are made from simpler intermediate metabolites such as amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides.
The end products of anabolic metabolism are organic molecules such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. The organism uses them for growth, movement, and reproduction processes.
What are the Organic Molecules Involved in Metabolism?
Organic molecules are compounds that contain carbon; these include proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, vitamins, and hormones.
Proteins
Proteins are organic molecules with a large variety of different functions in our body, including structural support. It breaks down into amino acids and can be used for energy and cellular purposes.
Proteins are the most abundant organic compounds in your body, and they are involved in vital processes. These processes include metabolism, DNA replication and repair, cell growth, and division.
These molecules are made up of amino acids used to create new proteins or break them down for energy purposes.
Proteins can take on a variety of shapes and forms. For example, they can be;
- A strand of hair
- The protein haemoglobin in our blood.
- A structure in our cells, such as the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Hormones in our body, such as insulin and adrenalin.
- Either soluble or insoluble in your bloodstream, which depends on the structure of the molecule.
- Enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms
- Antibodies to fight off disease and infections
Proteins have two main types, Alpha and Beta protein.
Alpha proteins are globular and soluble in water. They have many functions, but the main ones include catalysis, regulation of cell signals, and storage of substances.
Beta proteins are more rigid in shape and insoluble in water. They mostly have a structural role in the cell, such as the cytoskeleton.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. More than ten amino acids are classified into three categories; essential, conditionally essential, and nonessential.
Lipids


Lipids are organic molecules that contain one or more long chains of hydrocarbons. These fats can be either saturated, unsaturated, or polyunsaturated. Saturated fats are mostly found in animal products such as butter, beef, eggs, and cheese.
Unsaturated fats are found in plant-derived foods such as vegetables, nuts, seeds, and soybean oil. Polyunsaturated fats are found in canola oil, corn oils, and fish.
Lipids are mainly used for storing energy or as structural materials in the cell membrane.
The three common types of lipids are:
- Fats or triglycerides can be either saturated or unsaturated.
- Phospholipids and glycolipids are involved in the transport of lipids and other molecules.
- Cholesterol is a lipid that surrounds all cell membranes to form an oily semipermeable membrane.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic molecules that contain a large number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They can be categorized as either simple or complex carbohydrates.
Simple sugars are the most common type of carbohydrate, and it is found in a variety of foods such as fruit and milk. Simple sugars are called so because they are the simplest forms of carbohydrates. They can either be monosaccharides or disaccharides.
Polysaccharides, which include starches and cellulose, can be either simple or complex. The complex carbohydrates are found in the cell walls of plants. They also include;
- Cellulose is made from glucose and is the main component of plant cell walls. It is insoluble in water and is not digestible by humans.
- Glycogen can be broken down to produce energy. It’s made up of glucose and is found in animal cells.
- Lectins are carbohydrates with high antigenic activity, mostly found in foods such as legumes.
Vitamins
Vitamins are organic molecules involved in metabolic processes. They are organic compounds that the human body can’t synthesize. Vitamins are needed for growth, development, and a healthy lifestyle.
The most important vitamins for metabolism are:
- Vitamin A is important for eye health and helps to maintain the structure of cells.
- Vitamin B12 is useful for the production of DNA and RNA.
- Vitamin C helps with metabolism. It’s also an antioxidant that prevents damage to cells.
- Vitamin D is necessary for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus.
Hormones
Hormones are signalling molecules that can control a variety of reactions that occur in living organisms. They can be secreted externally from glands and organs, or the hypothalamus and pituitary glands can release them.
Some of these molecules are soluble in water and are carried through the bloodstream to the target organ. Others are insoluble in water and cannot be carried through the bloodstream.
Hormones are classified as either peptide or lipid-based.
- Peptide hormones are small in size, and they include;
- Glucagon is a hormone that increases blood sugar levels.
- Insulin hormone increases glucose uptake by cells.
Growth hormones and other polypeptides, such as exogenous insulin, are a hormone that lowers blood sugar levels.
Lipid hormones are larger and include;
- Thyroid hormone plays a role in metabolism and other vital processes in living organisms.
- Testosterone, the main male sex hormone, can also affect metabolism.
Inorganic Molecules in Metabolism


Inorganic molecules are those that don’t contain carbon. They can be either in the form of atoms, ions, or small groups of atoms.
Minerals are inorganic molecules that can be found in the body. They include;
- Iron is important for metabolism and oxygen transport.
- Calcium is found in the teeth and bones.
- Sodium regulates water levels in cells and blood pressure.
- Potassium controls muscle movements and balances the acid-base balance.
- Phosphorus is found in DNA and RNA molecules. It also helps to form bones and genetic material.
Plant Metabolism


Plants use a process called photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy. This process is the most important of plant metabolism. It provides the energy that is needed to survive.
Photosynthesis takes place in plant cells called chloroplasts, which are found in the leaves of the plant and contain chlorophyll and other pigments. This biological process starts with the absorption of light used to release energy from water molecules.
The water molecules are broken down in a series of steps, and the oxygen is released as a by-product.
This breakdown process generates an electron for every hydrogen, and when this happens, electrons are stripped from the water molecule. After that separation, the plants create more chemical energy that can be stored as electron carriers.
The end products of photosynthesis are:
- Energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- Oxygen is released as a by-product.
- Carbon dioxide is used for the synthesis of carbohydrates.
Ways of Increasing Metabolism


There are many ways to increase the metabolic rate in your body. Eating healthy and regular exercising can help with this. Focusing on foods that are rich in nutrients and vitamins will fasten metabolism and make you feel lighter.
Some of these foods include;
- Blueberries are high in vitamin C, fibre, and antioxidants.
- Salmon, is high in protein.
- Oatmeal contains soluble fibre that can decrease blood sugar levels and regulate appetite.
Regular and consistent exercising helps to increase metabolism through the use of energy-producing chemical reactions in the cells.
Other ways of boosting metabolism are:
- Eating breakfast. Skipping breakfast can cause a decrease in blood glucose levels which slows down metabolism.
- Having a high-fibre diet, which is important for regulating the body’s digestive system and decreasing inflammation.
- Drinking plenty of fluids can aid in digestion and elimination processes and eliminate toxins from the body.
- Stimulants such as caffeine and green tea.
- Taking supplements like L- carnitine, which is a vitamin that helps with fat metabolism.
Common Metabolism Terms
Inborn error of metabolism
Inborn errors of metabolism are genetic diseases that involve the disruption or malfunctioning of one or more enzyme systems. Some inherited metabolic disorders, such as phenylketonuria and galactosemia, are categorized as inborn errors of metabolism.
Basal metabolism
One way to measure the amount of energy released by a person’s body when they are resting. The basal metabolic rate (BMR) is based on the number of calories burned to maintain life processes.
The BMR can vary between individuals and may depend on age, gender, height, and weight. It can be measured by:
- Rest for 15 minutes in a warm environment with your eyes closed and then measure the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your breath.
- Pulse measurement (using two fingers on a wrist) to measure the body’s circulation.
Oxidative metabolism


The process in which organisms break down food for energy. It is the opposite of anaerobic metabolism, where oxygen is not present. Oxidative metabolism is the most common form of metabolism in living things.
This process occurs in the mitochondria, which are found inside cells and are started by the electron transport chain. During this process, electrons are transferred from one molecule to another, and ATP molecules are used to provide energy.
Anaerobic metabolism


Anaerobic metabolism is the process in which organisms break down food for energy without oxygen present. It is the opposite of oxidative metabolism, which is when oxygen is present.
The process occurs most often in single-cell organisms and multicellular plants. It takes place in the cytoplasm of cells. During this process, molecules are broken down by enzymes without the use of oxygen.
The products of anaerobic metabolism are lactic acid (pyruvic acid) and other substances such as hydrogen gas (H).
Intermediary metabolism


Intermediary metabolism is the use of energy from organic substances to build other compounds. This process is used by organisms that cannot create their food or break down other compounds to get energy.
Organisms use intermediary metabolism when they need to make amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. They also use it to break down carbohydrates and lipids, which are the main energy sources for animals.
Organisms that use intermediary metabolism are classified as prokaryotes, archaea, and some eukaryotic organisms. Organists use oxidative or anaerobic metabolism to break down food for energy.
Metabolic burst
Metabolic burst is a sudden increase in metabolism that happens when animals take flight from predators. The running animal’s muscles work harder and need more oxygen to sustain the increased activity.
This burst lasts for a few minutes, and then the animal’s metabolism returns to its original rate. Metabolic burst is also called “flight or fight response.”
Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis is when the pH of the blood drops and hydrogen ions (H) increase. This imbalance can be due to various causes, including kidney failure, liver disease, or diabetes mellitus. This condition is also called metabolic alkalosis.
The main sign of metabolic acidosis is a decrease in hydroxyl ions (OH) and hydrogen ions (H). A drop in the concentration of H can interfere with living cells by stopping them from performing their functions. The most common treatment for metabolic acidosis is intravenous fluids.
Metabolic alkalosis
A condition where the pH of the blood increases and hydroxyl ions (OH) decrease. The main symptom of this condition is an increase in the number of hydroxyl ions and a decrease in hydrogen ions.
Metabolic alkalosis can be caused by a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood due to hyperventilation, which is when you breathe too quickly. The most common treatment for metabolic alkalosis is to have the person breathe more slowly.
You may also be interested in Metabolic Pathways
Summary
Metabolism is one of the most complicated and important concepts in all of biology. It’s an essential part of every living organism on this planet, dictating how it grows, digests food, and stores energy. Metabolism can be broken down into two main categories: catabolic metabolism (the breakdown) and anabolic metabolism (building up molecules).
Though each type of metabolism has its specific function within the body, they are often intertwined as multiple pathways. They occur simultaneously to maintain homeostasis for a cell or organ system. Read more about the different types of metabolisms and understand how living organisms sustain life.


I‘m a freelance content and SEO writer with a passion for finding the perfect combination of words to capture attention and express a message. I create catchy, SEO-friendly content for websites, blogs, articles, and social media. My experience spans many industries, including health and wellness, technology, education, business, and lifestyle. My clients appreciate my ability to craft compelling stories that engage their target audience, but also help to improve their website’s search engine rankings. I’m also an avid learner and stay up to date on the latest SEO trends. I enjoy exploring new places and reading up on the latest marketing and SEO strategies in my free time.